

What is EPA's Action Level for Radon and What Does it Mean?
Radon in air is ubiquitous (existing or being everywhere at the same time). Radon is found in outdoor air and in the indoor air of buildings of all kinds. EPA recommends homes be fixed if the radon level is 4 pCi/L (picocuries per liter) or more. Because there is no known safe level of exposure to radon, EPA also recommends that Americans consider fixing their home for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L.
The EPA also recommends testing for radon every two years even if you have a mitigation system installed in your home.
EPA Radon Information
The U.S. EPA and the U.S. Geological Survey have evaluated the radon potential in the U.S. and have developed this map is to assist National, State, and local organizations to target their resources and to assist building code officials in deciding whether radon-resistant features are applicable in new construction. This map is not intended to be used to determine if a home in a given zone should be tested for radon. Homes with elevated levels of radon have been found in all three zones. All homes should be tested regardless of geographic location. The map assigns each of the 3,141 counties in the U.S. to one of three zones based on radon potential. Each zone designation reflects the average short-term radon measurement that can be expected to be measured in a building without the implementation of radon control methods. The radon zone designation of the highest priority is Zone 1.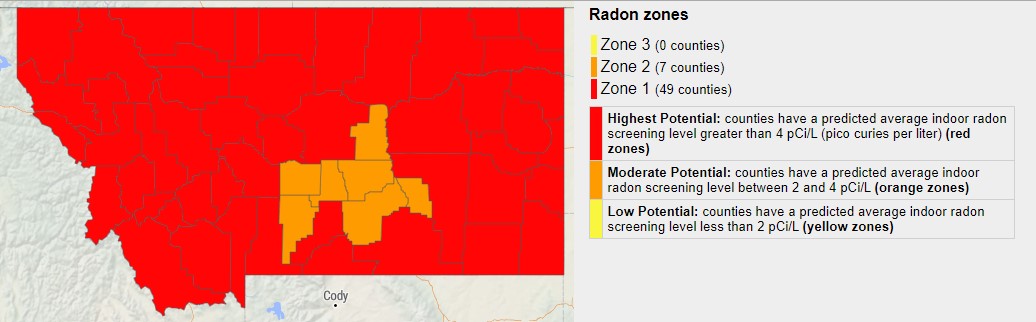
Important: Consult the EPA Map of Radon Zones document (EPA-402-R-93-071) before using this map. This document contains information on radon potential variations within counties. EPA also recommends that this map be supplemented with any available local data in order to further understand and predict the radon potential of a specific area. This and other indoor air quality publications can be ordered through the IAQ INFO Clearinghouse.

